This tutorial is aimed to teach one how to install Docker in CentOS 9 base host, and to perform basic tasks.
Quick Notes:
- You cannot run a Windows based container on a Docker that is installed in a Linux OS which used a Linux Kernel.
- You can run any Linux flavor based container on top of a Docker installed on any flavor of Linux.
- Docker images are templates that can be used to deploy containers.
- Multiple containers can be deployed using a same image
Pre-requisites:
- A new host with CentOS 9 minimal installation, 4GB RAM, 100 GB Hard disk.
- Ensure host is accessible via putty
- Disable Selinux and firewall
Update the host’s kernel
CentOS 9 based Installation
========*****========
Install minimal version of CentOS 9 on a VM.
Update all packages
[root@centos9docker ~]# dnf config-manager –add-repo=https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo
[root@centos9docker ~]# docker -v
Docker version 27.0.3, build 7d4bcd8
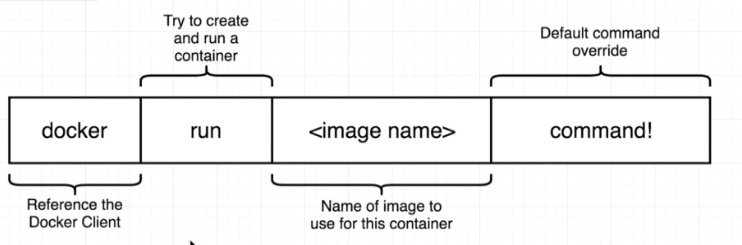
Let us try to run an image named hello-world. If the image is not present in localhost, the application will check in Docker repository and download hello-world container image.
[root@centos9docker ~]# docker run hello-world
===== ===
Unable to find image ‘hello-world:latest’ locally
latest: Pulling from library/hello-world
c1ec31eb5944: Pull complete
Digest: sha256:1408fec50309afee38f3535383f5b09419e6dc0925bc69891e79d84cc4cdcec6
Status: Downloaded newer image for hello-world:latest
Hello from Docker!
This message shows that your installation appears to be working correctly.
To generate this message, Docker took the following steps:
1. The Docker client contacted the Docker daemon.
2. The Docker daemon pulled the “hello-world” image from the Docker Hub.
(amd64)
3. The Docker daemon created a new container from that image which runs the
executable that produces the output you are currently reading.
4. The Docker daemon streamed that output to the Docker client, which sent it
to your terminal.
To try something more ambitious, you can run an Ubuntu container with:
$ docker run -it ubuntu bash
=== ==== ==
Similarly, let us download and run a small Ubuntu server, opening it in a console view:
[root@docker1 ~]# docker run -it ubuntu
The command Ctrl+PQ will allow us to exit from the Ubuntu host’s console. However the server will continue to run, and the Ubuntu image will continue to run. Instead, if we type “exit” instead of Ctrl+PQ the container will stop and you will get back to the base node’s cli.
Try both the situations and check the status of containers running on the node by issuing the command “docker ps“.
Let us run a container from image ubuntu and list out the directories in it when the container comes up
[root@docker1 ~]# docker run ubuntu ls
[root@docker1 ~]# docker run ubuntu ping google.com
Let us list the containers running on the docker. Take a note of the “NAME” field.
[root@docker1 ~]# docker ps
[root@docker1 ~]# docker ps -aq
Below command will list all containers ever created.
[root@docker1 ~]# docker ps –all
Below command will remove an image named hello-world
[root@docker1 ~]# docker rmi -f hello-world
The below command will allow us to get back to the container named “thirsty_ptolemy” if it is shown as running when the above command was executed.
[root@docker1 ~]# docker attach thirsty_ptolemy
Once in the container’s console, the command “exit” will stop the container, and exit out of its shell. Now the command “docker ps” will not display the container named “thirsty_ptolemy”.
root@bb06e23e73e2:/# exit
Lists the images available in the host
[root@docker1 ~]# docker images
Remove the “hello-world” image from the host.
[root@docker1 ~]# docker rmi -f hello-world
************ ***********
The below is an exerciser to create a small image from a set of files, that will be later used to run as container
[root@docker1 ~]# mkdir /sandbox
[root@docker1 ~]# cd /sandbox
[root@docker1 hello-system]# vi index.js
Add the below contents between the lines
===== ====== ====== ===
var http = require(‘http’);
const PORT = 80;
function requestHandler(req, res) {
res.end(`Hello my ${process.platform}`);
}
var server = http.createServer(requestHandler);
server.listen(PORT, function(){
console.log(`${process.env.NODE_ENV} server listening on port: ${PORT}. CTRL-C to exit.`);
});
===== ====== ====== ===
[root@docker1 hello-system]# vi package.json
This is copied from :
https://github.com/HermantNET/hello-system/blob/master/package.json
===== === ========= ======= ======== ======
{
“name”: “hello-system”,
“version”: “1.0.0”,
“description”: “Greets the current operating system”,
“main”: “index.js”,
“scripts”: {
“start”: “NODE_ENV=production node index.js”,
“test”: “echo \”Error: no test specified\” && exit 1″
},
“repository”: {
“type”: “git”,
“url”: “github.com/hermantnet/hello-system”
},
“author”: “Thomas E Herman Jr”,
“license”: “ISC”
}
===== === ========= ======= ======== ======
[root@docker1 hello-system]# vi .Dockerfile
=======**=======**===
FROM node:4-onbuild
EXPOSE 80
=======**=======**===
Now let us build the image, and look for the confirmation message “Successfully tagged hello-system:latest”
[root@docker1 hello-system]# docker build -t hello-system -f ./.Dockerfile .
Let us run the image
[root@docker1 hello-system]# docker run -it –rm –name shiju-running-app hello-system
This should run the image in its console view with the message at the end “production server listening on port: 80. Press CTRL-C to exit.”
Pressing CTRL+C should bring you back to your host’s shell prompt.
On basis of message displayed in the docker’s console view, you may not be able to check the website using “http://localhost:80”, etc.
You will have to create the container mapping a free port in the base host with the port 80 listened by the container, as shown below:
[root@docker1 /]# docker run -it -p 1337:80 –name myContainer hello-system
Now the website can be accessed using “http://localhost:1337”
Pressing CTRL+C should bring you back to your host’s shell prompt, but the container may be still running though the command “docker ps” wont list this container as running.
[root@docker1 hello-system]# docker ps
[root@docker1 /]# docker run -it -p 1337:80 –name myContainer hello-system
Note: This may give an error stating the container is running.
Below trick will remove the container completely
[root@docker1 /]# docker start myContainer
[root@docker1 /]# docker rm -f myContainer
The docker run command creates a container and starts it. The command to create a container is docker create <image> and the command to run it is docker start <container ID>.
Imagine you have changed the content in the “index.js” file to display a webpage “Hello my system Linux”. This will not come into action just by restarting the container. You will have to build a new docker image from the files, or run the following command, binding the folder holding the content to a place where the app will be located.
[root@docker1]# docker run -it -p 1338:80 -v /root/hello-system/.:/usr/src/app –name myContainer hello-system
Check the site accessing the base host via port 1338
List all containers hosted in the system, weather running or not:
[root@docker1 docker]# docker container ls -all
Remove a container named myContainer2
[root@docker1 docker]# docker rm -f myContainer2